What IsMobile Network Operator (MNO)?
A Mobile Network Operator (MNO) refers to a telecommunications entity that provides users with wireless voice, video, and data services.
Also known as wireless carriers or wireless service providers, MNOs normally own all the components they need to host and deliver their services to subscribers. These can include elements such as radio spectrum allocation and wireless network infrastructure.
These providers have cellular towers installed throughout a region to ensure there are no coverage gaps.
How Do Mobile Network Operators Work?
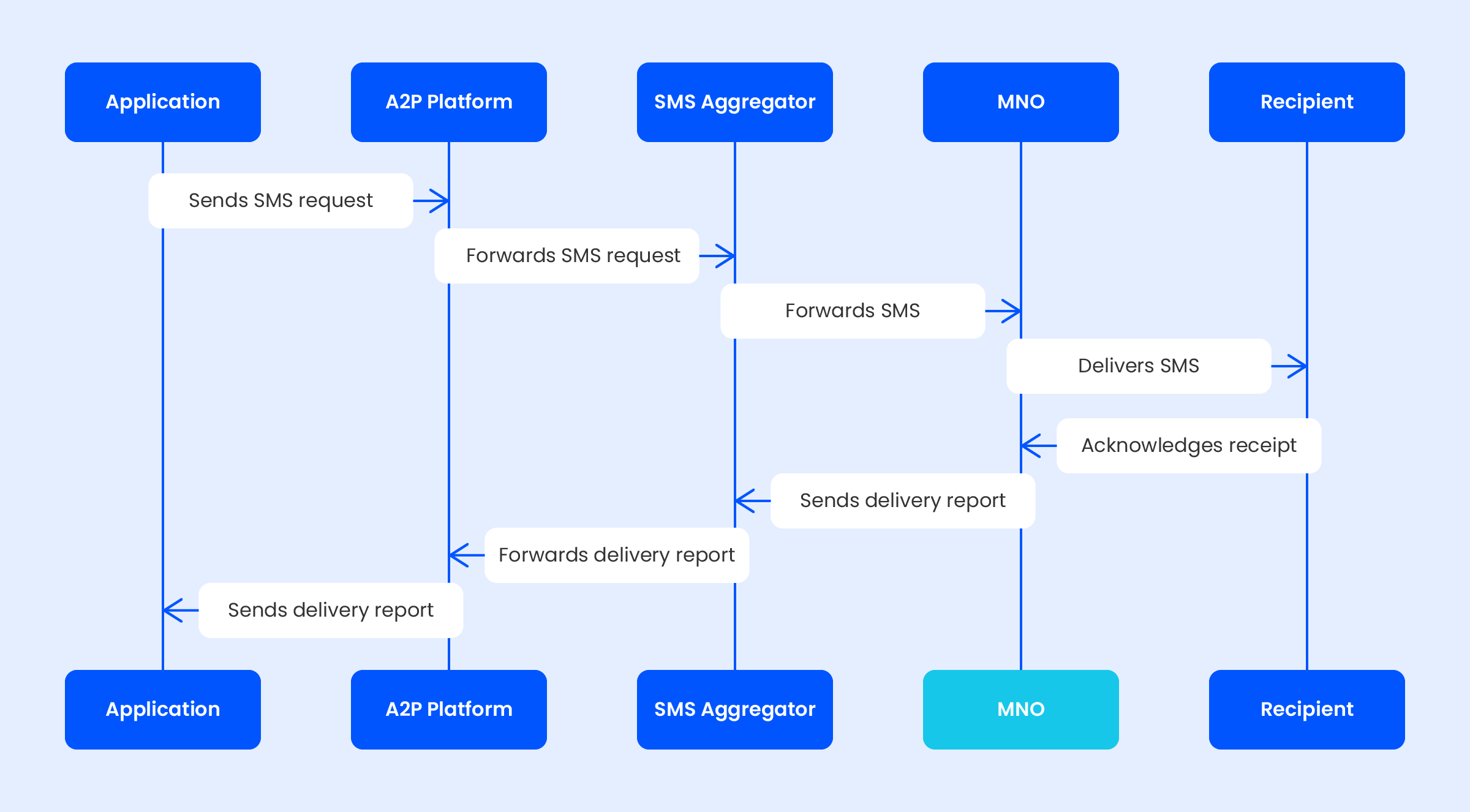
MNOs form a communication network to distribute telecommunications services among subscribers. They do this by creating an infrastructure that consists of base stations and transmitter masts, along with the necessary software.
Each device in the network would have a unique code known as an IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity). This code essentially allows the end-users to access the service with which they have an agreement.
Non-local subscribers, on the other hand, would require a roaming deal between the carrier they are connected to and the provider they are subscribed to.
MNOs Vs. MVNOs
An MNO normally makes use of an end-to-end network that it owns along with its radio and core infrastructure. This allows the provider to have full control over the coverage it provides in any geographical area.
These operators buy a frequency spectrum from local authorities and use those licensed frequencies to operate the wireless service. Carrier frequencies enable base stations or cell towers to communicate signals and generate coverage in any location.
A few examples of these providers include Verizon, T-Mobile, Etisalat, Orange, Vodafone, and Telefonica.
Unlike full-service carriers, virtual network operators do not own a full radio network. While they may have their own core infrastructure, MVNOs often purchase radio capacity from MNOs. Instead, they make use of the MNO’s base stations for coverage.
A virtual network operator may choose between becoming a light-touch reseller or a full MVNO with a core network along with branding, sales channels, billing, and so on. This depends on the amount of control they prefer to have.
Regardless of which option a virtual network operator chooses, their cellular coverage always depends on that of the host MNO. Using Telefonica’s radio network, the UK’s Tesco Mobile is one example of an MVNO.