What IsHLR?
A home location register (HLR) refers to subscribers that are authorized to use a global system for a mobile (GSM) core network. HLR is a database that contains subscriber information.
HLR Telecommunications Definition
HLR stands for "Home Location Register," and it is a crucial component in telecommunications networks, specifically in the context of mobile and cellular communication systems. The HLR is a database that stores essential information about subscribers who are part of a mobile network.
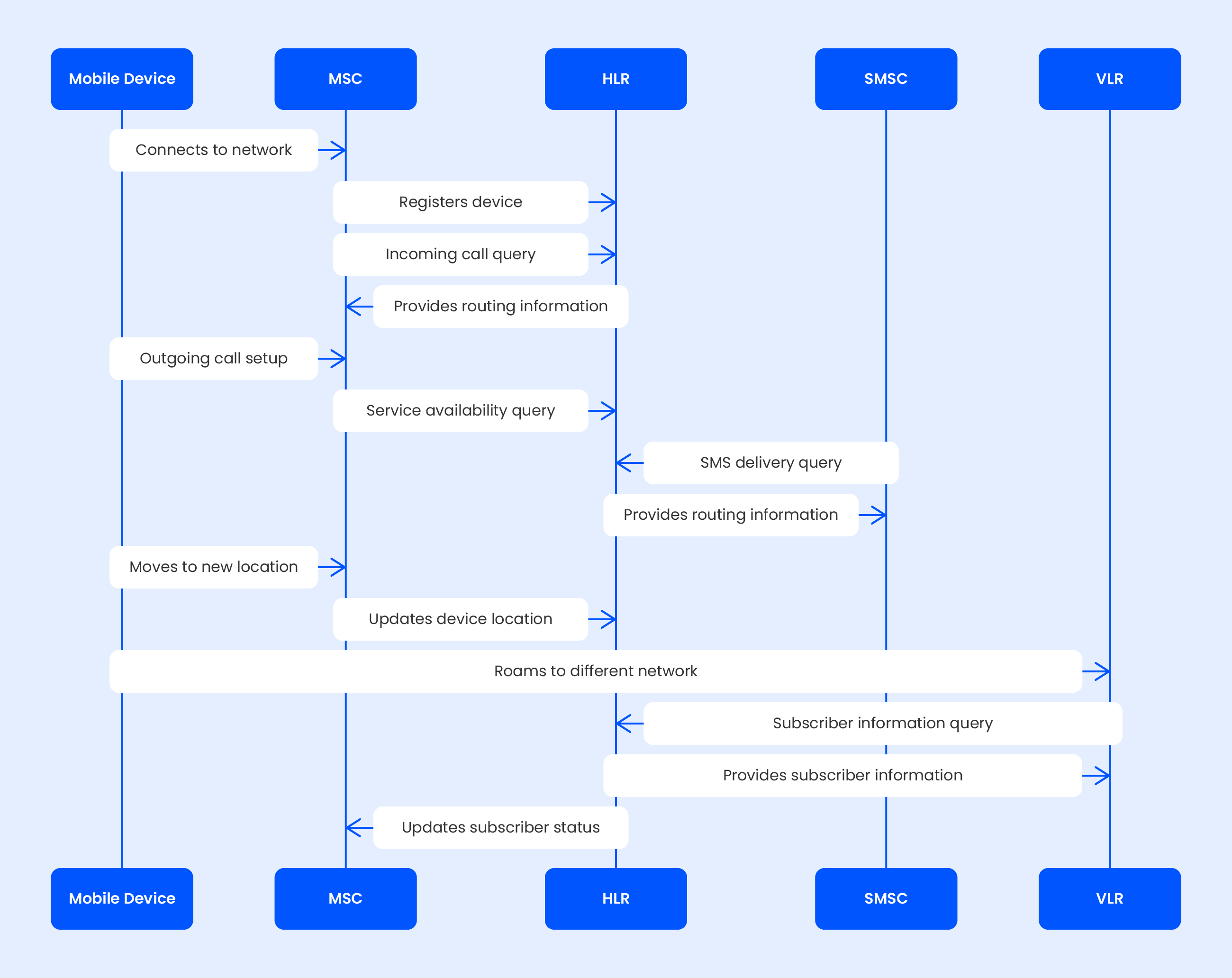
In a mobile network, each subscriber is associated with a home location, which is essentially the network operator they are subscribed to. The HLR contains various subscriber-related data, including subscriber and location info, subscriber services and ststus, romaning and security info.
When a call, text message, or data request is made to a subscriber's mobile number, the network consults the HLR to determine the subscriber's location and whether they are reachable. This information is crucial for the network to properly route calls, messages, and data to the subscriber's current location.
The HLR database includes:
- International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
- The phone number associated with the Mobile Subscriber Integrated Services Digital Network (the MSISDN)
- Account status
- Call divert settings
- Services requested by or rendered to the corresponding subscriber
- General packet radio service settings of the subscriber
- Last known location
As long as the subscriber remains connected with the mobile network operator, the data can be easily accessed.
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is the information that identifies each Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
The Mobile Subscriber Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) is the phone number you use to connect with a specific mobile user. The primary number is used for making and receiving voice calls and SMS. You can use a second for fax and data communication.
Functions of HLR in Telecom
HLR in telecom serves as the database for subscriber parameters. It includes customer ID, number, billing details, and the current recharge of the prepaid user. Moreover, it is the master database of all the subscribers to the GSM PLMN. The main database that contains permanent information about the subscriber—including the type tech with 2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G—is in GSM.
It is a component of 2G and 3G. However, 4G networks have a separate database called Home Subscriber Service (HSS), and 5G makes use of Unified Data Management (UDM) to manage network user data in a single, centralized element. This technology is identical to the 4G's HSS—the difference is that it's cloud-native and particularly intended for 5G.
As an important component for every subscriber, in mobile communication it is a database of every active customer of a mobile network. The Message Switching Center (MSC) uses the network’s database to identify the subscriber and authorize access to services. It also determines what to charge for which service and how to route the transmission to and from devices. When a contract ends with a carrier, the subscriber is removed, cutting access to the network.
If a subscriber belongs to a mobile network operator’s roaming partner, the databases don’t include information about the subscriber in these cases. When the local MSC checks with its Visitor Location Register (VLR), it requests the subscriber information from the home network. The VLR then confirms whether the device is allowed to attach to the network and verify the SIM. The database sends information to the VLR regarding what service the particular SIM can use, and the VLR temporarily stores the information.